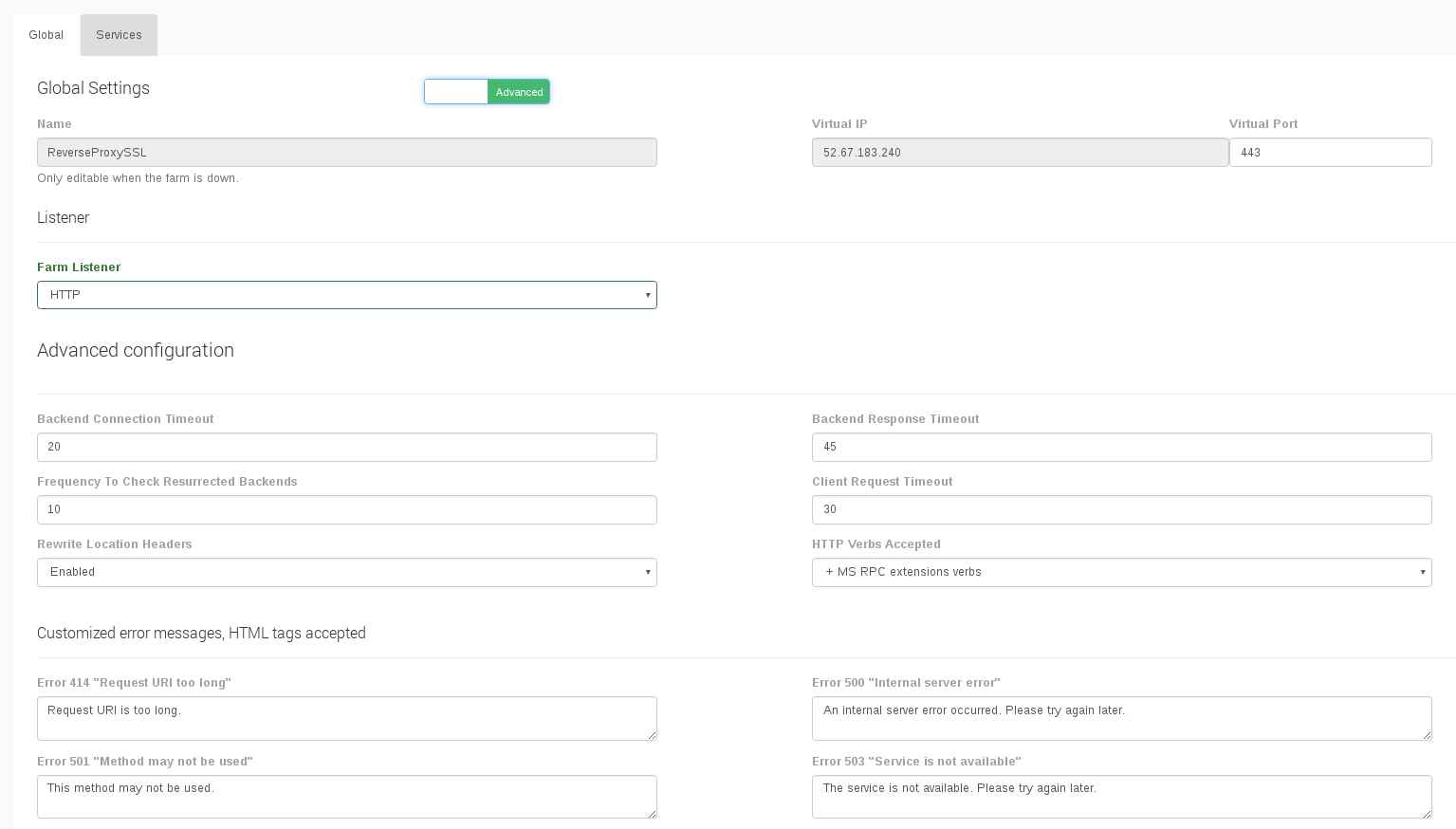
Global Settings for HTTP Farm Profile
This profile manages content switching at HTTP layer 7 application delivery for both HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
When modifying any parameter in a HTTP/S farm through the Update green button at the bottom, it would be needed a manual restart in order to apply the changes, so a defined status will be shown in the Menu Section LSLB Farms. The system administrator is able to modify whatever parameters are needed and then restart the farm service to apply all of them at the same time and when the time is more suitable.
After applying all these changes, please click on the Restart button and a message of success will be shown if the restart has been successfully done.
In the HTTP(S) farms profile, the HTTP header X-Forwarded-For is filled by default with the client IP address. By contrast with the L4xNAT farms profile, the HTTP profile use a weight algorithm implicitly.
Every HTTP(S) farm (or virtual service) is able to manage several web services through the same HTTP farm like a reverse proxy, therefore one HTTP virtual IP and port could handle more than one load balanced web service. For that reason, a service under a HTTP farm is a concept in order to offer the virtual host flexibility and then a list of backends will be shown for each service created.
The parameters for advanced HTTP/S farms profile are the following:
- Name. It’s the identification field and a description for the farm service.This value can't be change once the farm is created.
- Virtual IP and PORT. These are the virtual IP address and/or virtual PORT in which the farm profile will be binded and listening in the load balancer system. To make changes in Virtual Port value, ensure that the new virtual PORT is not in use. In order to apply the changes the farm service will be restarted automatically.
- Listener. This field specifies the protocol to be managed at layer 7 for content switching.
- HTTP. The virtual service will only understand plain HTTP content.
- HTTPS. The virtual service will understand secure HTTP content, it’ll manage SSL handshake, it’ll handle secure ciphers configurations, SSL certificates (wildcard or SNI), etc, in order to perform SSL offload and unload the real application servers of these heavy tasks.
- Rewrite Location headers. If enabled, the farm is forced to modify the Location and Content-location headers in responses to the clients. If they point to the backend itself or to the VIP (but with a different protocol) the response will be modified to show the virtual host in the request. If the option enabled and compare backends is selected then only the backend IP address is compared, this could be useful for redirecting a request to an HTTPS listener on the same server as the HTTP listener.
- HTTP verbs accepted. This field indicates the operations that will be permitted to the HTTP client requests. If a not allowed verb is requested an error will be shown to the client.
- Standard HTTP request. Accept only standard HTTP requests (GET, POST, HEAD).
- + extended HTTP request. Additionally allow extended HTTP requests (PUT, DELETE).
- + standard WebDAV verbs. Additionally allow standard WebDAV verbs (LOCK, UNLOCK, PROPFIND, PROPPATCH, SEARCH, MKCOL, MOVE, COPY, OPTIONS, TRACE, MKACTIVITY, CHECKOUT, MERGE, REPORT).
- + MS extensions WebDAV verbs. Additionally allow MS extensions WebDAV verbs (SUBSCRIBE, UNSUBSCRIBE, NOTIFY, BPROPFIND, BPROPPATCH, POLL, BMOVE, BCOPY, BDELETE, CONNECT).
- + MS RPC extensions verbs. Additionally allow MS RPC extensions verbs (RPC_IN_DATA, RPC_OUT_DATA).
- Backend connection timeout. This value indicates how long the farm is going to wait for a connection to the backend in seconds. Usually, it will be the socket opening time wait. By default, this value will be set to 20 seconds.
- Backend response timeout. This value indicates how long the farm is going to wait for a response from the backends in seconds. By default, this value will be set to 45 seconds.
- Frequency to check resurrected backends. This value in seconds is the period to get out a blacklisted real server and checks if is alive. The farm will be checking the backend periodically once the real server is marked as down, regardless of whether there is a new client connection or not. By default, this value will be set to 10 seconds.
- Client request timeout. This value indicates how long the farm is going to wait for a client request in seconds. Once this timeout is reached without getting any data from the client, the connection will be closed. By default, this value will be set to 30 seconds.
- Personalized error messages. Through the personalized error messages, the farm service is able to answer a custom message of your site when a web code error is detected from the real servers. A personalized HTML page will be shown.
By other hand, some HTTPS Parameters can be found below.
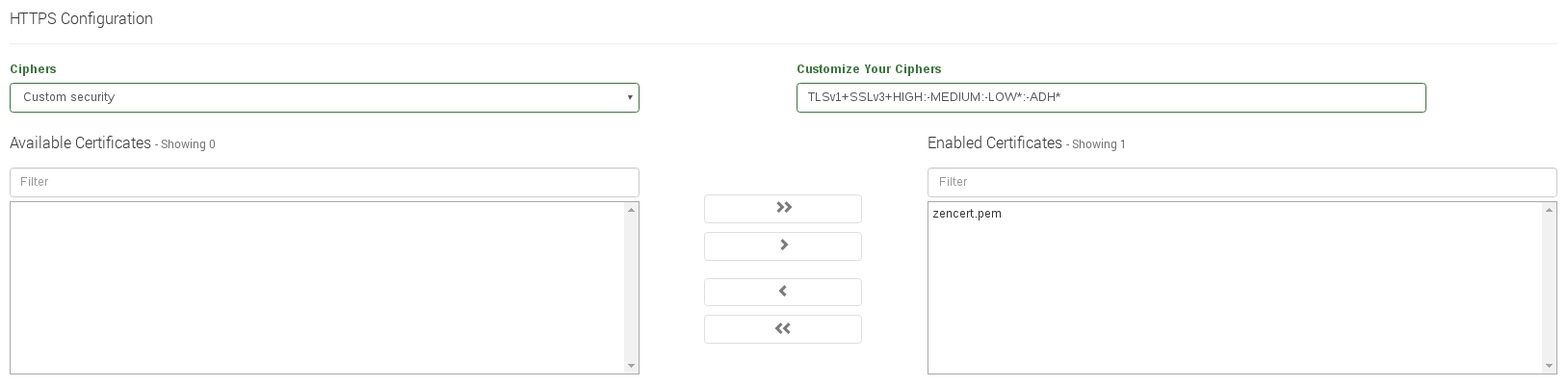
- Ciphers. This field is used to build a list of ciphers accepted by SSL connections in order to harden the SSL connection. In order to make use of ciphers please select one of the following options.
- All. This item indicates that all ciphers are allowed to be managed by the HTTPS listener. This is the default setting.
- High security. This option set by default the ciphers: kEECDH+ECDSA+AES128:kEECDH+ECDSA+AES256:kEECDH+AES128:kEECDH+AES256:kEDH+AES128:kEDH+AES256:DES-CBC3-SHA:+SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!LOW:!kECDH:!DSS:!MD5:!EXP:!PSK:!SRP:!CAMELLIA:!SEED. Which they’ll be enough to pass through an A+ in ssllabs .
- Custom security. This option allows to set your own allowed ciphers through the Customize your ciphers field. By default this value will be ALL
- Customize your ciphers. This is the allowed customized list of ciphers that will be accepted by the SSL connection, which it’s a string in the same format as in OpenSSL ciphers . This option will be displayed if Custom security is set.
- Enabled certificates. The SSL certificates in this list will be the certificates that the farm will be able to manage.
- Available certificates. These are the available SSL certificates installed in this virtual Load Balancer.
There is a dedicated section where the administrator can upload more certificates to the Load Balancer if needed, supporting PEM formar without passphrase. ZVNcloud is able to support any kind of certificate, SSL simple multidomain or wildcard.
Services for HTTP Farm Profile
The services within a LSLB farm with HTTP profile provides content switching capabilities for web virtual services to deliver multiple web services and applications through thesame virtual IP and PORT, which helps to unify web applications through one single domain, manage virtual hosts, manage URLs, configure redirects, configure persistence and backends per service. Every service within a LSLB farm could have different properties, health checks or backend list, and some regular expressions can be used as match conditions that can specify which service should be used per request.
Every service match condition will be checked by the HTTP farm profile core in priority mode (that can be altered if needed) and if none service is matched then the farm core will return an error. For this reason, specific multiple service definitions are allowed. If no URL is defined then every request will match. The HTTP service conditions will be determined by a virtual host and/or an URL pattern.
Firstly, it’s required to create at least one service in order to add backends.
After the creation, it’ll be asked to Restart the farm in order to apply the new service.
Once the new service is applied, the HTTP farm profile will parse every service conditions in order to match the correspondent service for each client request. Those services conditions could be determined by URL patterns, specific headers or redirection and allows to identify several web services in through the same farm.
The service conditions and options for HTTP farms profile are shown below.
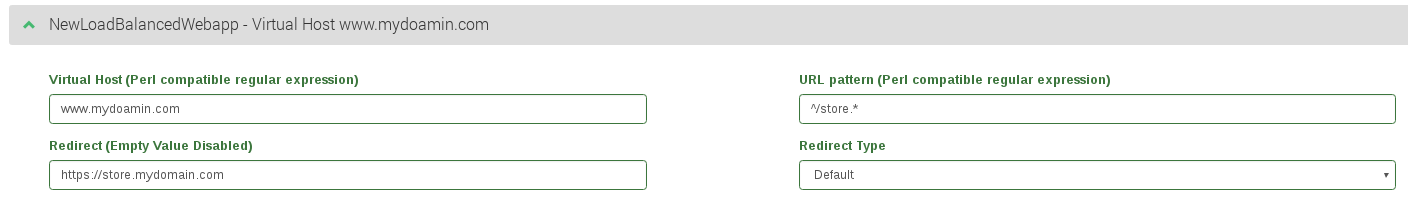
- Virtual Host. This field specifies the condition determined by the domain name through the same virtual IP and port defined by a HTTP farm. In order to discard this condition just leave it empty. This field supports regular expressions in PCRE format.
- Url pattern. This field allows to determine a web service regarding the URL the client is requesting through a specific URL pattern which will be syntactically checked. In order to discard this condition just leave it empty. This field supports regular expressions in PCRE format.
The Virtual Host and URL pattern fields are used by ZVNcloud in order to take decisions at the time of match to a certain service, so if any value is configured in these fields the request will try to match it, if it doesn’t match the request will try to match to the next service. It’s recommended to include a last service as the default one if no match has been produced.
- Redirect. This field behaves as a special backend, as the client request is answered automatically by a redirect to a new URL. If you configure a redirect value thenDON’T configure backends in this service. If Virtual Host and URL pattern match then ZVNcloud sends an HTTP Location Header response to the client in order to be redirected to the configured URL.
- Redirect Type. There are two options: Default or Append. With Default option, the URL is taken as an absolute host and path to redirect to. With Append option, the original request path will be appended to the host and path you specified.
- Least Response. This checkbox enables an improvement of round robin algorithm. Dynamically, the load balancer establishes the connection with the lower value of response time.
- HTTPS Backends. This checkbox indicates to the farm that the backends servers defined in the current service are using the HTTPS protocol and then the data will be encrypted before to be sent.
- Persistence. This parameter defines how the HTTP service is going to manage the client session and which HTTP connection field has to be controlled to maintain safe client sessions. When a type of persistence session is selected a persistence session TTL will be shown.
BASIC: Basic authentication. The HTTP basic authentication header will be used to control the client sessions. For example, when a web page requests a basic authentication to the client a HTTP header will contain a string like the followin:
No persistence: The farm service won’t control the client sessions and the HTTP or HTTPS requests will be free delivered to real servers.
IP: Client address. The client IP address will be used to keep open the client sessions through the real servers.
HTTP/1.1 401 Authorization Required
Server: HTTP/1.0
Date: Sat, 27 Nov 2011 10:18:15 GMT
WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="Secure Area"
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 31
Then the client answer with the header:
GET /private/index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost
Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ==
URL: A request parameter. When the session ID is sent through a GET parameter with the URL will be possible to use this option indicating the parameter name associated with the client session ID. For example, a client request like http://www.example.com/index.php?SESSION_ID=3a5ebc944f41daa6f849f730f1 should be configured the parameter Persistence Session Identifier: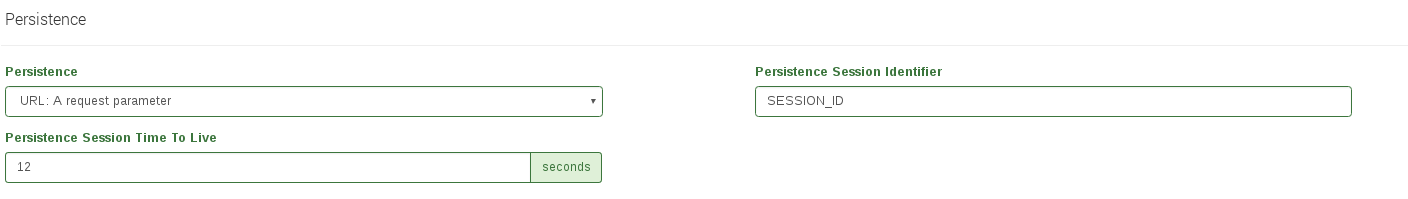
PARM: an URI parameter. Another way to identify a client session is through an URI parameter separated from a semicolon character that is used as a user session identifier. In the example http://www.example.com/private.php;EFD4Y7 the parameter will be used as the session identifier.
COOKIE: a certain cookie. Also, you’ll be able to select an HTTP cookie variable to maintain the client session through the COOKIE option. A cookie has to be created by the real app programmer into the webpage to identify the client session, for example:
HEADER: a certain request header. An HTTP header custom field could be used to identify the client session. For example:
GET /spec.html HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.org
Cookie: sessionidexample=75HRSd4356SDBfrte
- Persistence Session Time To Live. This value indicates the max time of life for an inactive client session (max session age) in seconds.
- Persistence Session Identifier. This field is the URL parameter, cookie or header field name that will be analyzed by the farm service and will manage the client session.
- Cookie insert. If defined, ZVNcloud HTTP farms profile will inject a cookie in each response with the appropriate key of the backend, so that even if the session table is flushed or sessions are disabled, the proper backend will be chosen. This feature avoids to change the real server code to create a session cookie.
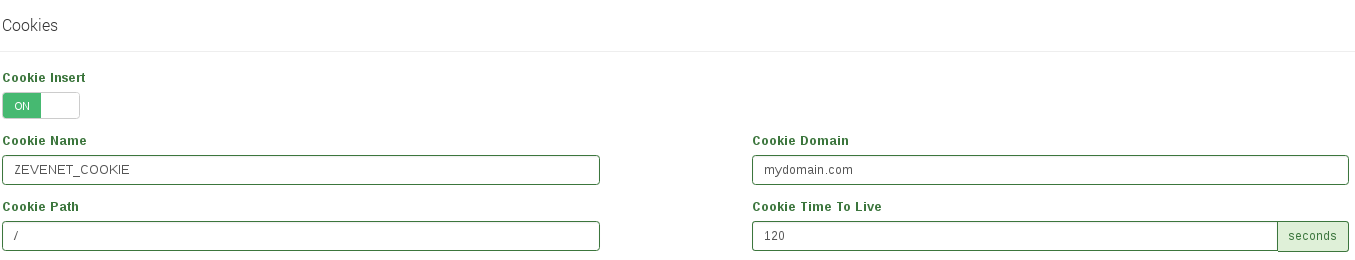
- Cookie Name is the name of the cookie that will be created from client to backend.
- Cookie Path is the URI or relative path where the new cookie will be created, for the whole domain the character / needs to be set.
- Cookie Domain is the domain where the cookie is going to be created. Finally,
- Cookie Time to live is the number of seconds the cookie will be persisted in memory between the client and backend. If this value is set to 0, the cookie will expire when the browser closes.
After the service configuration, it’ll be required to update the changes through the green button Update.
Backend Servers Health Check
By default, Zevenet runs simple health checks to the backends or real servers, but sometimes this check is not enough to determine that the backends are working appropiately. For this reason, Zevenet implements a service that executes and manages advanced health checks via a daemon.
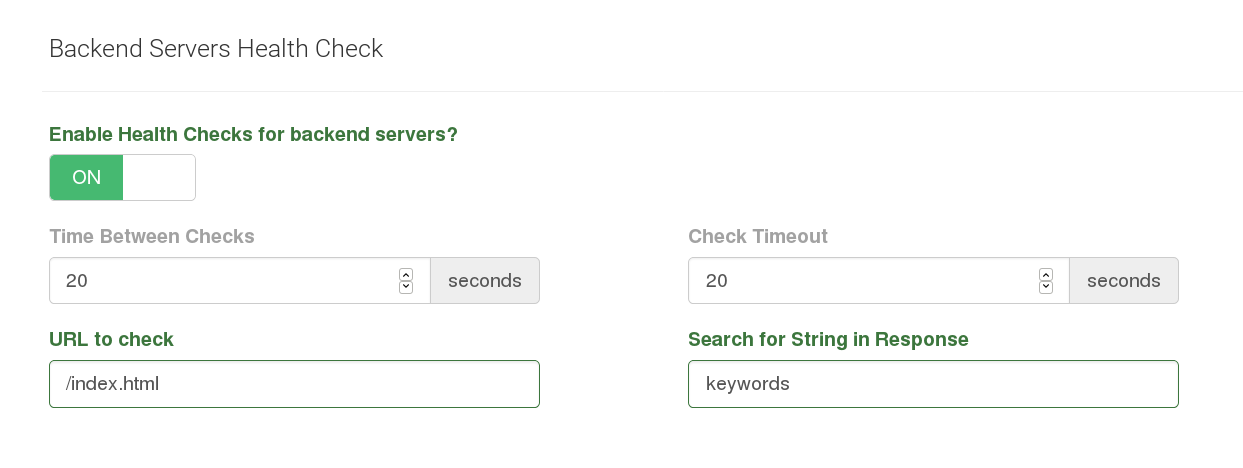
The fields of Health Checks are:
- Enable or Disable button: May be ON or OFF.
- Time Between Checks: Seconds from one check to the next.
- Check Timeout: Period of time in seconds that the daemon wait for a backend response before considering it is not responding.
- Search for String in Response: Daemon will search and parse the string in this field on the HTTP response body.
In the previous screenshot the checker send a GET to /index.html for each of the backends. Later it search the string "keywords" in the body of the response. If that string is found the check is consider successfull.
In regards to the Backends section, the HTTP farm profile allows to configure the following real servers properties:
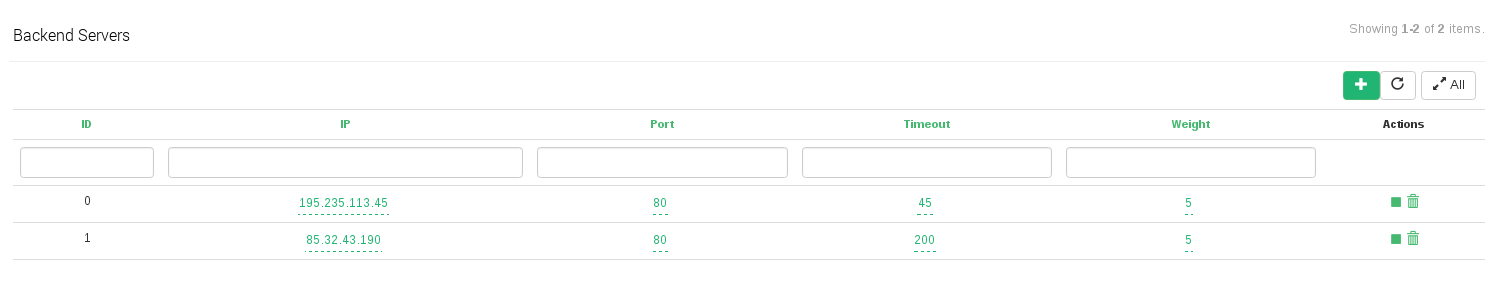
- ID. It’s the index that references the backend in the farm configuration, this field is not editable.
- IP. The IP address of the given backend.
- Port. It’s the port value for the current real server.
- Timeout. It’s the specific value of timeout for a backend to respond. This value overrides the global Backend connection timeout farm parameter for the current backend.
- Weight. It’s the weight value for the current real server. More weight value indicates more connections delivered to the current backend. By default a weight value of 1 will be set. The values range available are from 1 to 9.
- Actions. The available actions per backend are:
- Add Backend. Add a new real server into the farm.
- Save. Save the new real server entry in the given farm and start using it.
- Enable Maintenance. Put a certain real server in maintenance mode, so no new connections will be redirected to it.
- Start. Enable new connections to the real server again after the enabled maintenance.
- Delete. Delete the given real server of the virtual service.
- For editing. please click on the given field in the Backend Servers table and apply the changes


Comments